Latest Recommendation
Considered the best "sucrose substitute", do you know the advantages of allulose?
2021.09.29 | Starlight So True
In the past hundred years, with the development of the sugar industry and food industry, human dietary structure has changed rapidly, but genes have not yet fully adapted to this point. The intake of a large amount of refined sugar has induced many health problems: obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, etc. How to not only enjoy the joy of sweetness, but also avoid the troubles of obesity, "sucrose substitute" has become a major research focus of people's exploration, among which allulose is regarded as the best "sucrose substitute".

Image source: Pexels
What is allulose?
D-allulose is an epimer of fructose, which exists naturally in nature but has very little content. It has similar taste and volume characteristics to sucrose, and has 70% sweetness of sucrose. It can also undergo Maillard reaction with amino acids or proteins in food. It has very good crystallinity and powdery product characteristics.

After the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) officially approved D-psicose as Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) in 2011, in October 2020, the FDA issued a " Industry Guidance: Statement on the calories of psicose and psicose on nutrition and supplement labels", it is recommended that manufacturers exclude psicose from “total sugar” and “added sugar” on the label, and at the same time The calorie of psicose is set as 0.4 kcal/g.
Jim Carr, Director of Global Ingredient Technology for Taylor’s Sweeteners, said, “Allulose is very similar to sucrose. In addition to reducing calories, it also has a function very similar to sugar. Its sweetness intensity and sweetness curve are very similar to sucrose. , There will be no peculiar smell like other sweeteners. From a performance point of view, allulose also provides the same effect as sucrose in reducing water activity and browning." And these are stevia. The high-intensity sweetener does not have.
Unique advantage
Allulose is widely used in the U.S., Japan, and South Korea markets. It is mainly added to soft candies, beverages, bread, pastries, jelly, coffee and some medical foods. It is a new star of functional sugar that many well-known food ingredient companies are very optimistic about. Compared with other sugar substitutes, what is the advantage of allulose?

Image source: Pexels
①Close to sucrose sweetness + extremely low calories
Allulose has high sweetness (equivalent to 70% of the same amount of sucrose) and very low calories (the caloric value is only 0.4 kcal/g), does not cause blood sugar rise, and is a good functional sweetener .
The metabolic pathway of psicose in the human body is also different from other sugar substitutes. It is easily absorbed into the blood through the small intestine, 70% of which is excreted in urine and feces, and the remaining 30% is transported to the large intestine, but the microorganisms in the large intestine It has low fermentation utilization of psicose and can hardly be metabolized to produce energy [1]. These results show that D-psicose is almost not metabolized and does not provide calories after being absorbed through the intestines, so it will not cause gastrointestinal discomfort like sugar alcohol. This is the significant difference between D-psicose and other sugars, and it is also its most prominent advantage as an alternative sweetener.
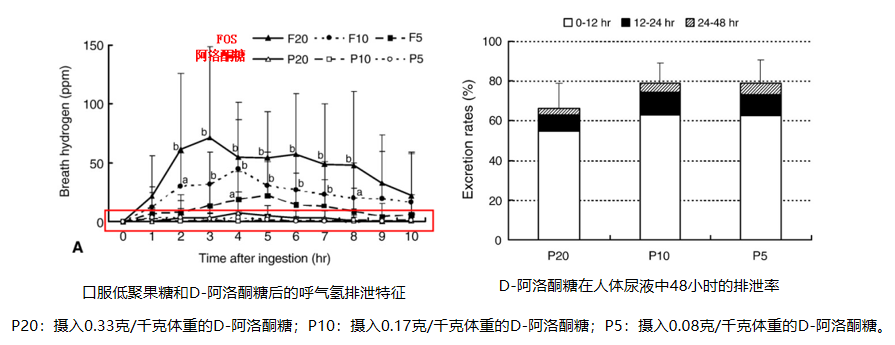
②Good taste + antioxidant properties
Allulose can provide food with proper sweetness, smooth texture, ideal taste and good shelf stability.
The addition of D-psicose in the soft candy formula helps the formation of the gel and the improvement of structural properties. Compared with sucrose, D-allulose can retain more water in the gel network [2]. Adding D-allulose to food also produces good flavor and high antioxidant substances, namely Maillard reaction products (MRPs). MRPs show strong free radical scavenging activity and reducing ability, which can be used as having excellent chemical and biological properties The functional ingredients are used in formula foods.
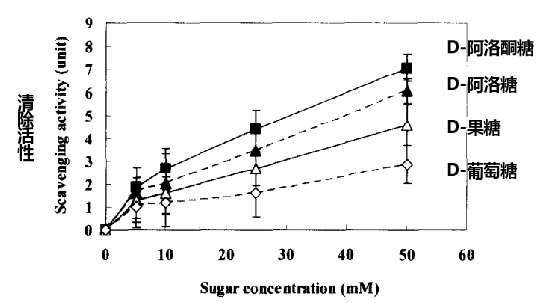
③Reduce blood sugar + lipid-lowering effect
According to the International Diabetes Federation (IDF), there are approximately 415 million adult patients with diabetes worldwide, and my country has the largest number of diabetes patients, about 110 million (11.6% of Chinese adults), and 493.4 million (50.1%) pre-diabetes population. [3] Metabolic diseases such as diabetes and overweight/obesity have become a global crisis.
Hayashi et al. [4] used a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled crossover experiment to explore the safety and effects of D-allulose on postprandial blood glucose levels in adult men and women, including patients with borderline diabetes. Twenty-six subjects drank zero or 5 grams of D-allulose in a standard diet, and compared the blood glucose levels of fasting and 30, 60, 90, and 120 minutes after a meal. It was found that D-allulose inhibited the postprandial blood glucose of patients with borderline diabetes. effect.
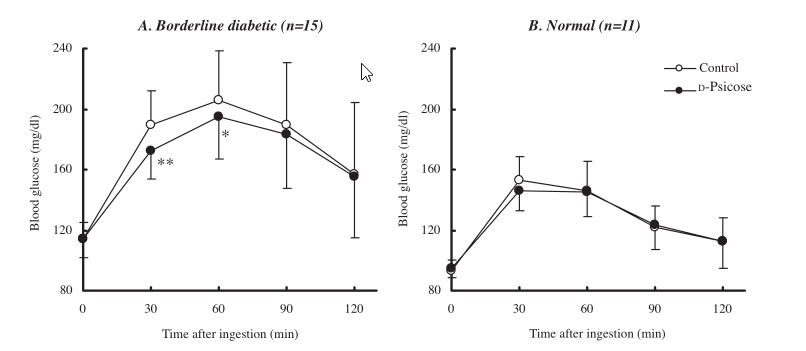
About So True
Shandong Starlight So True Biological Technology Co., Ltd. was established in 2016 and is affiliated to Shandong Starlight Sugar Industry Group. It has a number of independent research and development products with independent intellectual property rights, including prebiotic series: fructo-oligosaccharides, galacto-oligosaccharide, and isomaltose. ; Dietary fiber series: resistant dextrin, polydextrose; sugar-reducing ingredients series: allulose, isomaltulose; special sugar series, etc.
References
[1]Iida T. Failure of D-psicose absorbed in the small intestine to metabolize into energy and its low large intestinal fermentability in humans[J]. Metabolism Clinical and Experimental, 2010, 59:206-214.
[2]Ei A, Pp A, Mo B, et al. Role of 'D-allulose' in a starch based composite gel matrix[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 228.
[3]帅玉英, 孙怡, 吴晓花,等. 低热量甜味剂D-阿洛酮糖的生产应用研究进展[J]. 中国食品添加剂, 2014(9):159-163.
[4]Hayashi N, Iida T, Yamada T, et al. Study on the Postprandial Blood Glucose Suppression Effect of D-Psicose in Borderline Diabetes and the Safety of Long-Term Ingestion by Normal Human Subjects[J]. Journal of the Agricultural Chemical Society of Japan, 2010, 74(3): 510-519.

 Follow the wechat of So True
Follow the wechat of So True
